गहराई में: स्टॉप ऑर्डर्स रद्द क्यों किए जाते हैं
पारंपरिक बाज़ारों के विपरीत, क्रिप्टोकरेंसी बाज़ार 24/7 संचालित होता है। स्टॉप-लॉस और टेक-प्रॉफ़िट ऑर्डर का अच्छा इस्तेमाल करने से जोखिमों को काफी कम किया जा सकता है और समय की बचत हो सकती है। यह मार्गदर्शिका KuCoin स्टॉप-लॉस/टेक-प्रॉफ़िट सिस्टम का विवरण देती है और उन शर्तों को समझाती है जिनके तहत स्टॉप ऑर्डर रद्द किए जा सकते हैं।
परिदृश्य 1: अपर्याप्त फंड्स
परिदृश्य 2: KuCoin कीमत सुरक्षा पार हो गई
परिदृश्य 3: बाज़ार की अस्थिरता के दौरान ऑर्डर भरने में असमर्थ या अप्रत्याशित रूप से मूल्य भरने में असमर्थ
परिदृश्य 1: अपर्याप्त फंड्स
नए अपडेट्स: हम इस लिंक को फॉलो करके KuCoin के स्टॉप-लॉस/टेक-प्रॉफ़िट फ़ीचर के नए अपडेट्स की समीक्षा करने की सलाह देते हैं।
अपग्रेड के बाद, स्टॉप ऑर्डर सेट करते समय आपके फंड्स फ़्रीज़ नहीं किए जाते हैं। स्टॉप ऑर्डर ट्रिगर होने पर ही फंड्स फ़्रीज़ किया जाता है। हालांकि, ट्रिगर होने के समय अपर्याप्त फंड्स उपलब्ध होने पर ऑर्डर रद्द कर दिए जाएंगे।
उदाहरण: टॉम के ट्रेडिंग खाते में 32,000 USDT हैं और BTC की मौजूदा कीमत 31,000 USDT है। रेजिस्टेंस तोड़ने के बाद कीमत 35,000 USDT तक बढ़ने की उम्मीद करते हुए, वह 32,000 USDT के रेजिस्टेंस स्तर पर स्टॉप लिमिट ऑर्डर सेट करता है। यह देखते हुए कि BTC की कीमत काफी स्थिर बनी हुई है, टॉम फिर इसका फ़ायदा उठाने के लिए 30,000 USDT उधार देता है, जिससे उसके खाते में केवल 2,000 USDT रह जाते हैं।
जब BTC आख़िरकार 32,000 USDT तक पहुंच जाता है, तो टॉम के स्टॉप ऑर्डर को ट्रिगर किया जाना चाहिए था। दुर्भाग्य से, सक्रिय उधारी देने के कारण, उपलब्ध बैलेंस अब ऑर्डर के पहले सेट किए जाने की तुलना में कम है, और अब ट्रिगर करने के लिए कम से कम 32,100 × 0.5 = 16,050 USDT (शुल्क को छोड़कर) की आवश्यकता होती है। नतीजतन, ऑर्डर रद्द कर दी गई है। इसी तरह, यदि फंड्स अन्य ओपन ऑर्डर्स या USDT ट्रेड्स के लिए अधिक एलोकेट किए गए थे, तो ऑर्डर भी रद्द कर दी जाएगी।
परिदृश्य 2: KuCoin कीमत सुरक्षा पार हो गई
बाज़ार की चरम स्थितियों में ट्रेडर्स के हितों की रक्षा करने के लिए, KuCoin स्पॉट मार्केट में इमीडीएटली एक्ज़ीक्यूटेबल प्राइस रेंज (IEPR) प्रणाली का इस्तेमाल करता है।
→ कीमत सुरक्षा के बारे में और जानें।
कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा = (अंतिम ट्रांज़ैक्शन कीमत - बेहतरीन खरीदी या बिक्री कीमत) / बेहतरीन खरीदी या बिक्री कीमत × 100%
1. स्टॉप-लिमिट ऑर्डर्स के लिए, ट्रिगर या लिमिट कीमत सेट करने पर कोई प्रतिबंध नहीं है। सिस्टम यह जांचता है कि नई ट्रांज़ैक्शन्स कीमतें KuCoin कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा से अधिक है या नहीं। यदि ऐसा है, तो कीमत सीमा के भीतर ऑर्डर का कोई भी हिस्सा निष्पादित किया जाएगा, और अतिरिक्त रद्द कर दी जाएगी।
उदाहरण: जैसा कि ऊपर दिखाया गया है, टॉम 10% की कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा के साथ BTC खरीदने के लिए स्टॉप-लिमिट ऑर्डर प्लेस करता है। वह 32,100 USDT की ऑर्डर बुक में मौजूदा बेहतरीन बिक्री कीमत पर अपनी ऑर्डर सेट करता है। ऑर्डर ट्रिगर होती है और ऑर्डर बुक में भरने के लिए भेजी जाती है। सिस्टम जांचता है कि ऑर्डर पूरी तरह से भरे जाने पर नई कीमत 35,400 USDT (10%) तक पहुंच जाएगी, 10.28% की बढ़ोतरी ([35,400 - 32,100] ÷ 32,100 के रूप में गणना की जाती है।) चूंकि पूरी भरी हुई ऑर्डर 10% की कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा से अधिक होगी, इसलिए जिस हिस्से के कारण यह सीमा पार हो जाती है, उसे रद्द कर दिया जाएगा।
2. स्टॉप-मार्केट ऑर्डर्स के लिए, सिस्टम यह भी जांचता है कि नई ट्रांज़ैक्शन कीमत KuCoin कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा से अधिक है या नहीं। यदि ऐसा है, तो कीमत सीमा के भीतर ऑर्डर का कोई भी हिस्सा निष्पादित किया जाएगा, और अतिरिक्त रद्द कर दी जाएगी।
उदाहरण: टॉम BTC खरीदने के लिए स्टॉप-मार्केट ऑर्डर सेट करता है, जिसकी कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा 10% है। ऑर्डर बुक में उपलब्ध बेहतरीन बिक्री कीमत 32,010 USDT है। जब BTC 32,000 USDT तक पहुंच जाता है, तो ऑर्डर ट्रिगर हो जाती है और ऑर्डर बुक भरने के लिए भेजी जाती है। यदि ऑर्डर 32,000 USDT पर सक्रिय होती है और 36,000 USDT तक भर जाती है, तो यह 12.46% बढ़ोतरी सीमा को पार कर जाता है (गिनती इस प्रकार: [36,000 - 32,010] ÷ 32,010 = 12.46%)। इस प्रकार, शुरुआती 10% बढ़ोतरी (35,211 USDT के बाद, 32,010 USDT × 110% के गिनती के अनुसार) से ऊपर का कोई भी हिस्सा रद्द कर दिया जाएगा।
परिदृश्य 3: ऑर्डर भरने में असमर्थ या बाज़ार की अस्थिरता के दौरान अप्रत्याशित भरने की कीमत
1. स्टॉप लिमिट ऑर्डर्स: एक बार ट्रिगर होने पर, वे लिमिट ऑर्डर्स बन जाते हैं। कीमतों में तेजी से उतार-चढ़ाव कभी-कभी इन ऑर्डर्स को पूरी तरह से भरने से रोक सकता है। ये ऑर्डर तब तक ओपन ऑर्डर्स बने रहते हैं जब तक कि वे पूरी तरह से भर नहीं जाते या अन्य शर्तों के अनुसार रद्द नहीं हो जाते।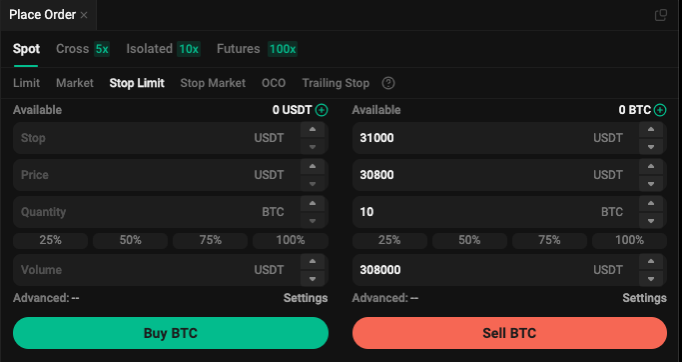
उदाहरण: टॉम स्टॉप लिमिट सेल ऑर्डर सेट करता है, जैसा कि ऊपर दिखाया गया है। निम्नलिखित तीन स्थितियाँ हो सकती हैं:
a. ट्रिगर कीमत तक पहुंचने के बाद BTC 30,800 USDT से ऊपर बढ़ जाता है, और ऑर्डर बुक से उपलब्ध बेहतरीन कीमतों पर ऑर्डर भरता है।
b. BTC 30,800 USDT के ट्रिगर कीमत के आसपास उतार-चढ़ाव करता है और इसके नीचे चला जाता है। यहां, ऑर्डर आंशिक रूप से 30,800 USDT से ऊपर के किसी भी बेहतरीन उपलब्ध कीमत से भर जाती है, और शेष राशि भरे जाने या रद्द होने तक ओपन ऑर्डर के रूप में रहती है।
c. ट्रिगर कीमत तक पहुंचने के बाद BTC तेजी से 30,800 USDT से नीचे गिर जाता है। इस स्थिति में, ऑर्डर ओपन रहती है और तभी भरती है जब कीमतें 30,800 USDT पर वापस आती हैं या उससे अधिक होती हैं।
2. स्टॉप मार्केट ऑर्डर्स: ये ऑर्डर्स ट्रिगर होने के बाद मौजूदा मार्केट कीमत पर भरे जाते हैं। इस मामले में, जब बाज़ार विशेष रूप से अस्थिर होते हैं, तो अपेक्षित मूल्य से विचलन का जोखिम हो सकता है। इस प्रकार, नई कीमत, कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा से अधिक होने पर ऑर्डर का एक हिस्सा रद्द किया जा सकता है।
उदाहरण: जैसा कि ऊपर दिखाया गया है, टॉम स्टॉप मार्केट बिक्री ऑर्डर सेट करता है। सबसे बेहतरीन उपलब्ध खरीदी कीमत 31,000 USDT है। कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा इससे 10% कम, 27,900 USDT पर सेट की गई है (गिनती इस प्रकार: 31,000 - [31,000 × 10%] = 27,900)। यहाँ से, निम्न स्थितियाँ हो सकती हैं:
a. ऑर्डर ट्रिगर होने के बाद BTC की कीमत 31,000 USDT से ऊपर बढ़ जाती है, और 31,000 USDT से नीचे बिना गिरे, बेहतरीन उपलब्ध कीमतों पर पूरी तरह से भरी जाती है।
b. BTC की कीमत 31,000 USDT के आसपास रहती है, लेकिन 27,900 USDT से कम नहीं होती है। परिणामस्वरूप, ऑर्डर बुक से उपलब्ध बेहतरीन खरीदी कीमतों से ऑर्डर पूरी तरह से भरी हुई है, जिसकी औसत कीमत 27,900 USDT से अधिक है।
c. ऑर्डर ट्रिगर होने के बाद भी BTC की कीमत में गिरावट जारी है, जो 27,900 USDT से नीचे जा रही है। चूंकि यह कीमत सुरक्षा सीमा से अधिक है, इसलिए सिस्टम केवल 27,900 USDT से ऊपर की कीमतों पर ऑर्डर का कुछ हिस्सा भरता है, और इस सीमा से नीचे निष्पादित होने वाले किसी भी शेष को रद्द कर देता है।